Introduction
In software development, Git is a widely used version control system that allows developers to manage and track changes in their codebase. Branching is a key feature of Git that allows developers to create separate lines of development for their code. Here, we'll dive deep into the basics of Git branching to help you understand how developers use this powerful tool.
But in the meantime don't forget to check this article out What is Git or GitHub if you are finding it difficult to grasp
What is Git Branching?
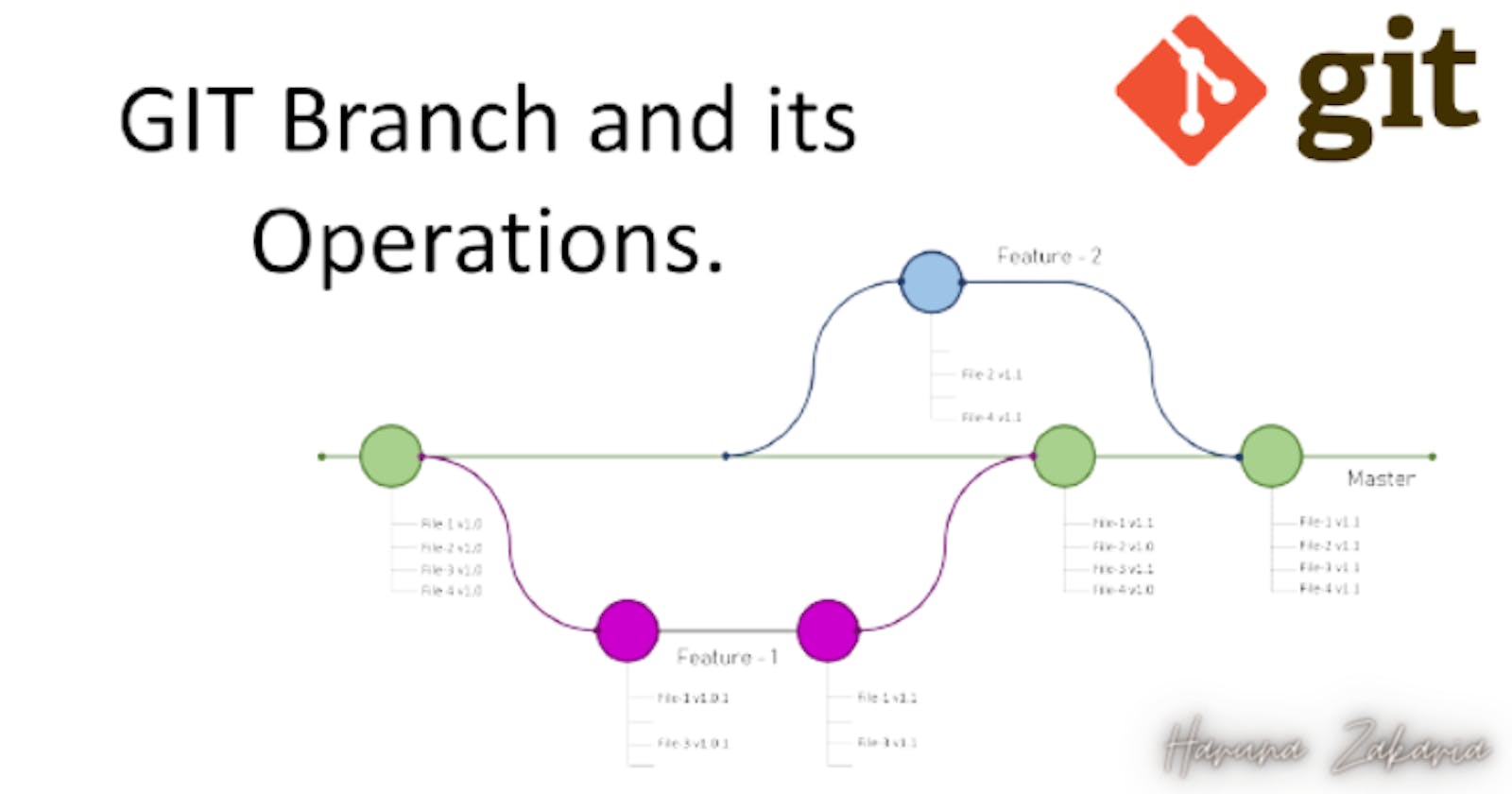
A branch is a snapshot of a project in time. When you create a new branch in Git, you’re essentially creating a copy of the project’s codebase, which you can then develop separately from the main codebase.
This allows you to work on new features, bug fixes, or experiments without worrying about impacting the main codebase.
Why Use Git Branching?
There are several reasons why developers use branches in Git. Here are a few:
Parallel Development: With branches, developers can work on multiple features or bug fixes in parallel. By splitting the codebase into separate branches, developers can avoid conflicts and reduce the time it takes to complete a project.
Isolated Changes: Branches allow developers to experiment with new features or make changes to code without impacting the main codebase. This means that if something goes wrong, the main codebase stays intact.
Testing: Branches are useful for testing new features or bug fixes. Before merging a branch into the main codebase, developers can run tests to ensure that the new code works as intended.
How to Create a Branch in Git
Creating a new branch in Git is quite simple. Here are the steps:
Open the Git Bash terminal or command prompt.
Navigate to the project’s directory with
cd project_directorycommand.Create a new branch with the command bellow
git branch <branch_name>Replace
<branch_name>with the name of the new branch, you want to create.Check out the new branch by using the command below
git checkout <branch_name>This git command lets you navigate between the main branch and the new branch that you have just created.
How to Merge a Branch in Git
Once you’ve made changes to a branch and tested them, you can merge the changes into the main codebase. Here are the steps:
Make sure you’re on the main branch (usually
master) by usinggit checkout masterMerge the changes by using the command
git merge <branch_name>Replace
<branch_name>with the name of the branch, you want to merge.Resolve any conflicts that arise during the merge.
Test the merged code to ensure that it works as intended.
Finally, commit the merged code to the main branch with the command.
git commit
Conclusion
Git branching is a powerful tool for developers that enables them to work on multiple features or bug fixes simultaneously. By creating isolated branches, developers can experiment with new ideas without impacting the main codebase. With Git branching, developers can work more efficiently and reduce the time it takes to complete a project.
If this article was helpful then don't forget to share it with your friends that might find it helpful too.
Also, subscribe to my newsletter so that you will always receive a direct email from me whenever I publish a new article. And If you'd like to talk, you may follow me on Twitter (@Harunzakaria) and send me a direct message.